Algorithms
Below are the algorithms that will be utilized in this project.
Sketch Recognition
To classify drawings we have implemented a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with around 100,000 parameters. This neural network was constructed with the help of the TensorFlow Keras library, exported for use in TensorFlowJS. This architecture consists of three convolutional layers followed by max-pooling layers to learn hierarchical features from the input image. Then, it flattens the output and passes it through two fully connected layers, with the final layer using softmax activation for class probabilities. The training data used was from the Google Quick, Draw! dataset. The model currently recognizes 38 different drawings which are all directly mapped to tiles in our dictionary. The model is lightweight enough to be run on mobile devices with a quick inference time. See the model architecture below.
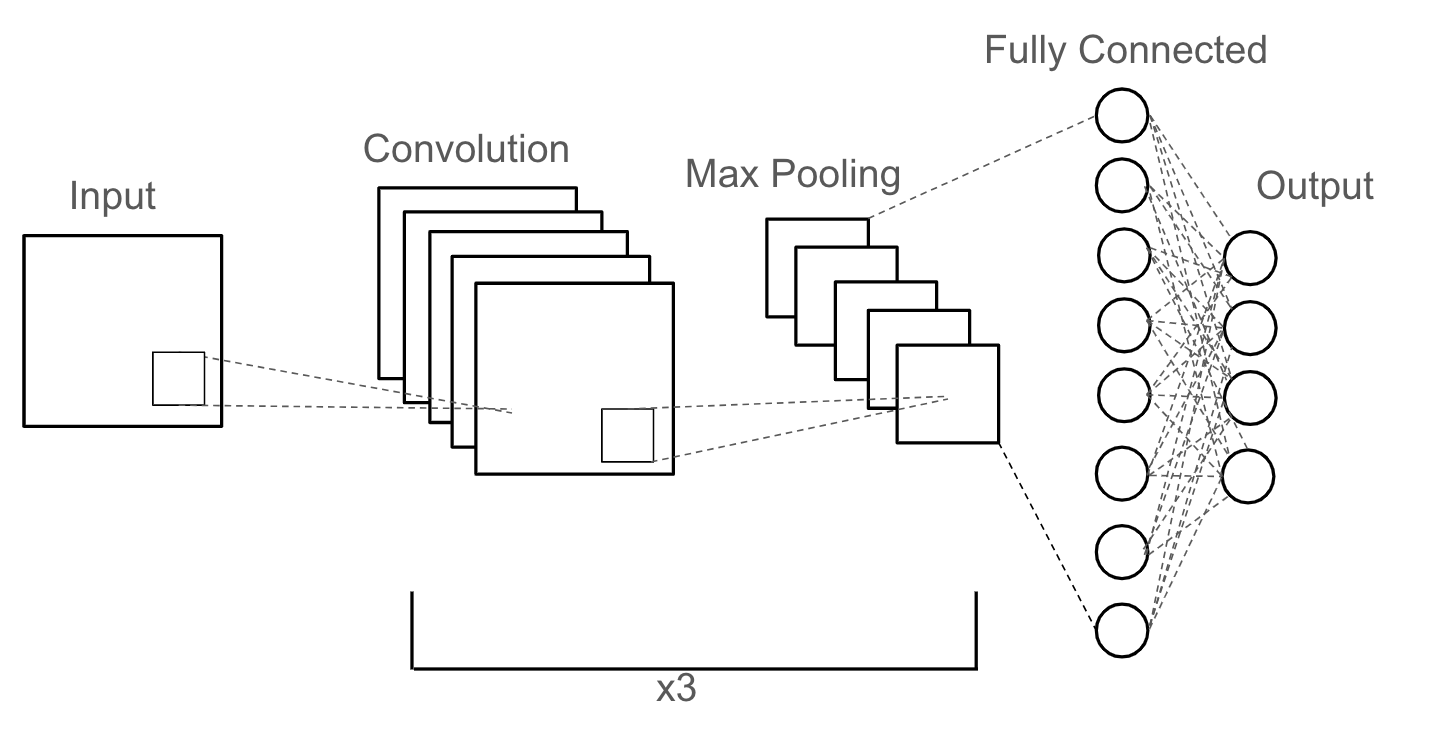
Image Recognition
To identify what objects are being captured by the devices camera, this project has implemented an image classifier to achieve this task. The model is connected to Amazon Rekognition API, which uses a pre-trained deep learning model to label and classify images in real time. Images are sent to an S3 bucket where they are analyzed and return a response with detected objects and their associated confidence values. To learn more about the model refer to Amazon Rekognition's documentation.
Word Similarity Search
In AAC, one image could represent a few different (but similar) words. For example, if someone drew a circle, we would want the system to suggest tiles such as 'circle', 'shape', or even 'ball'. Our image classification model may not always capture all of these possibilities. To get around this, we have implemented natural language processing (NLP) to capture context and similarly related words. We use the spaCy library to achieve this goal. The model essentially converts words into embedded vectors. Cosine similarity can be used between vectors to extract similar words.